SCS Blog
Recent SCS Blogs
Parylene vs HumiSeal®
The conformal coating process establishes a protective barrier for product substrates. The selection of coating material is influenced by various factors: HumiSeal® is a leading provider of conformal coating materials, offering a range of coating types. Among these, the acrylic-based 1B31 stands out for its popularity due to its ease of application and protective qualities.... Read More >>
Parylene and Silicone Conformal Coatings: A Comparison
One liquid coating type that rivals the use of Parylene is silicone conformal coating (Type SR), which cures rapidly, is reliably dielectric and displays exceptional stability across a wide temperature range. These properties make it Parylene’s chief performance competitor, for many purposes. Further comparison delineates their benefits and disadvantages relative to each other. Composition While... Read More >>
SCS Educational Opportunities
As a global industry leader in conformal coatings technologies, SCS provides multiple opportunities to learn about various coatings and the benefits they provide for applications in the aerospace, defense, electronics, automotive and medical device industries. If you’re interested in learning more, you’re invited to join us at any of the following events: On Demand: Conformal... Read More >>

Live Demos and Rep Award: Highlights of IPC APEX 2023
SCS recently exhibited at the IPC APEX Expo, held January 24-26, 2023, at the San Diego Convention Center in California. Throughout the show, SCS provided demonstrations of its PrecisionCoat VI coating and dispensing platform with the highly-flexible Automatic Quick Change (AQC) feature. With outstanding reliability and accuracy, the PrecisionCoat VI offers customers unmatched conformal coating... Read More >>
SCS Achieves Nadcap® Accreditation
SCS’ Indianapolis coating facility has achieved Nadcap® accreditation for conformal coating of electronics – printed board assemblies, demonstrating its continued commitment to quality. The Nadcap audit, conducted by industry experts, is a rigorous technical assessment and demands the highest standards of critical process control and validation. SCS Indianapolis attained the elite accreditation as a result... Read More >>

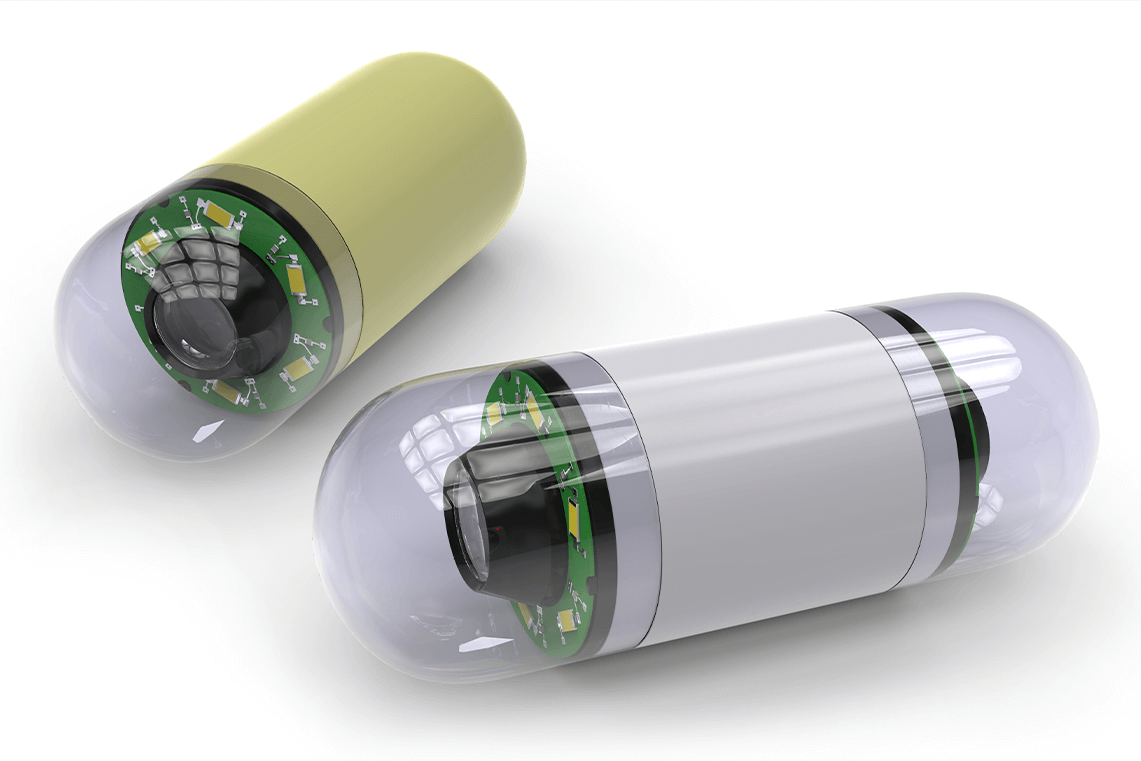
Parylene Protects Life-Enhancing Medical MEMS Technologies
Cutting-edge medical technologies provide a greater understanding of physiology through miniaturization and advanced diagnostics. Many of these technologies include the use of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) in fields like microfluidics, advanced bio-sensing and personalized medicine. Protecting sensitive MEMS devices from a variety of harsh conditions is essential for these technologies to be successful. Parylene and ALD+Parylene... Read More >>
SCS Announces New Plasma Nanocoatings at CES
In January, SCS exhibited at CES® in Las Vegas, Nevada. The show is known in the consumer electronics industry as the most influential tech event in the world and the proving ground for breakthrough technologies and global innovators. During the show, SCS announced the availability of its newest coating technology — PlasmaGuard™, an environmentally-friendly, halogen-free... Read More >>

Aerospace Conformal Coatings: Acrylic vs Silicone vs Parylene
Conformal coatings made of acrylic, silicone, and Parylene polymers play a crucial role in diverse aerospace applications, pushing technologies to their limits. These coatings, applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electrical assemblies, help uphold device performance under challenging operational conditions. Factors like atmospheric changes, chemicals, humidity, mobile ion infiltration, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and... Read More >>
Parylene for LEDs
LED Lifespan as Effected by UV Light LEDs are engineered to deliver up to 100,000 hours of light in ideal lab settings. Yet, their endurance diminishes significantly in real-world applications due to factors like electrical interference, moisture, UV light and physical damage. To maximize efficiency, LEDs need safeguarding against these persistent threats. Of all the... Read More >>
Optical Clarity of Parylene at Increased Thickness
Generally applied at micron-thin coating layers, Parylene offers numerous barrier, dielectric, insulative and similar protective benefits to printed circuit boards (PCBs) and related electronic assemblies. One property of Parylene applied in its normal range of 0.013 mm to 0.051 mm (0.0005 in to 0.002 in) is exceptional optical clarity, which makes it suitable for coating... Read More >>

